Succession Planning for Business Owners
Succession Planning for Business Owners
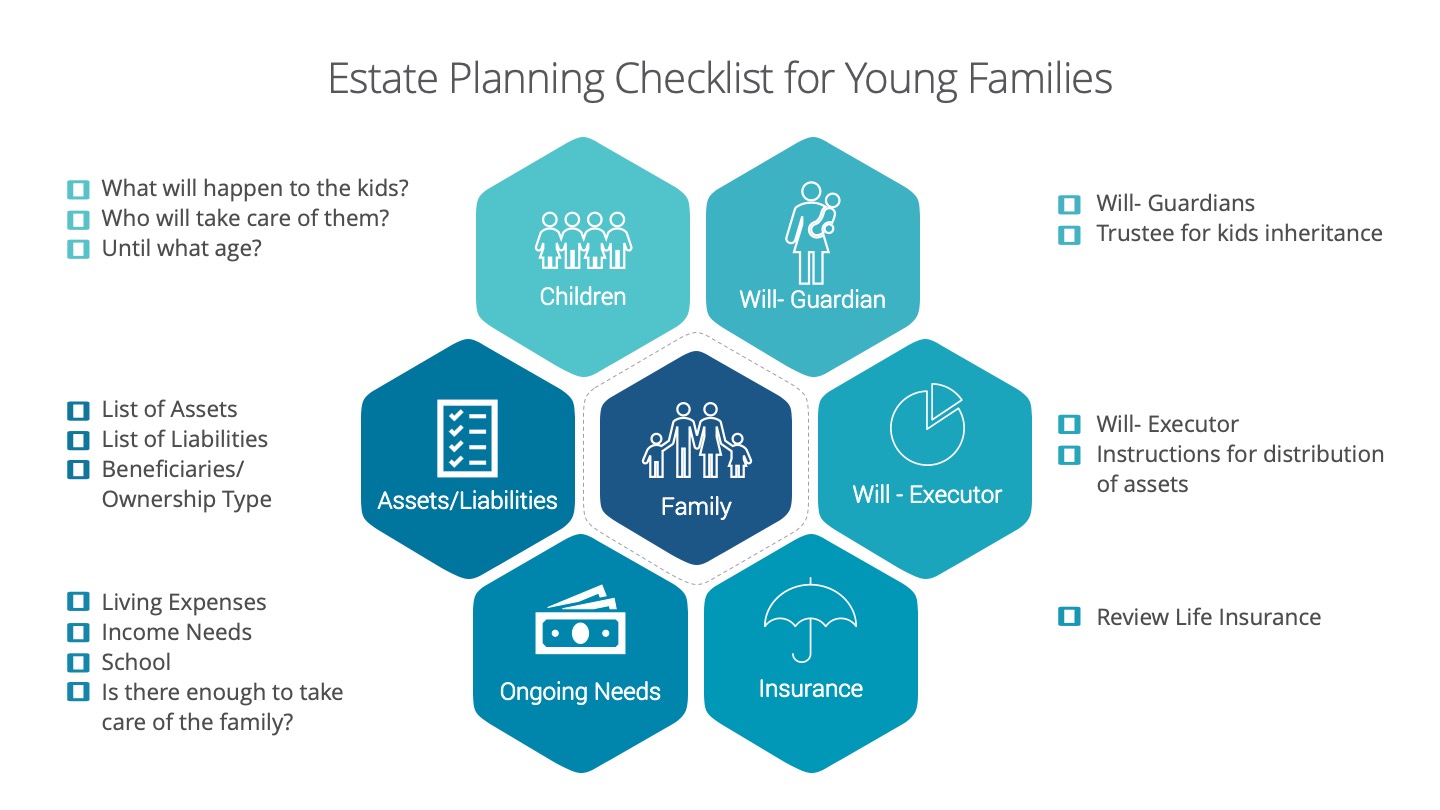
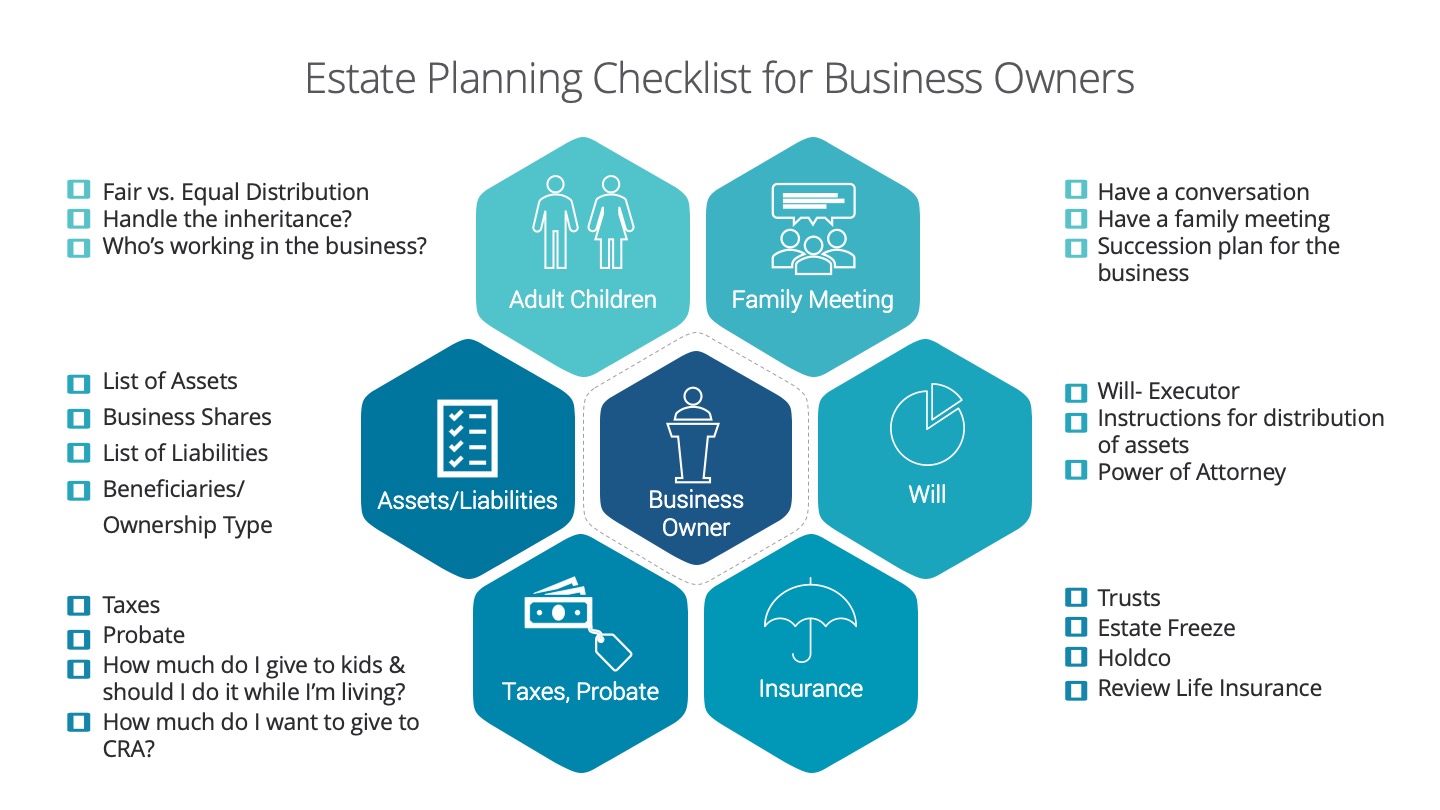
Business owners deal with a unique set of challenges. One of these challenges includes succession planning. A succession plan is the process of the transfer of ownership, management and interest of a business. When should a business owner have a succession plan? A succession plan is required through the survival, growth and maturity stage of a business. All business owners, partners and shareholders should have a plan in place during these business stages.
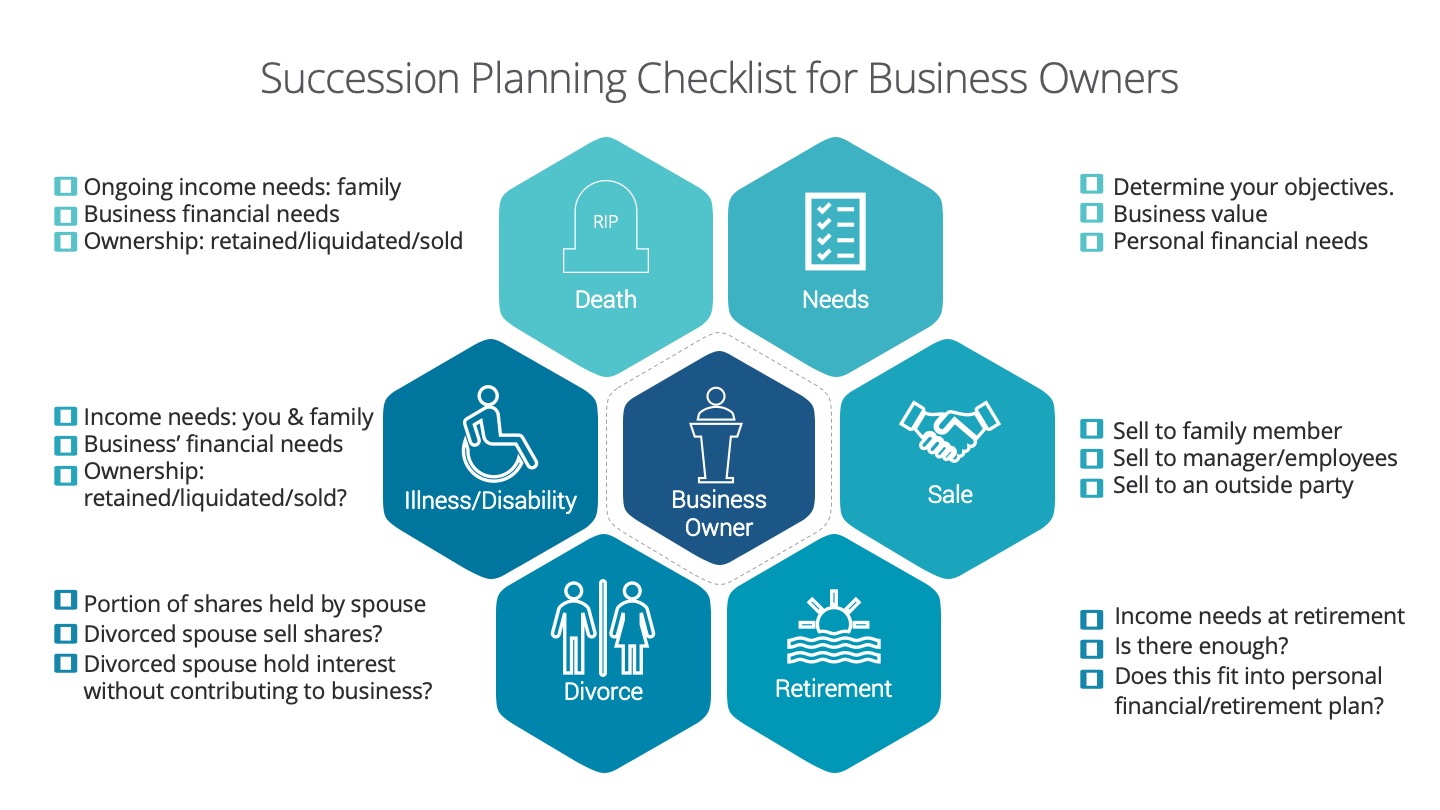
We created this infographic checklist to be used as a guideline highlighting main points to be addressed when starting to succession plan.
Needs:
-
Determine your objectives- what do you want? For you, your family and your business. (Business’ financial needs)
-
What are your shares of the business worth? (Business value)
-
What are your personal financial needs- ongoing income needs, need for capital (ex. pay off debts, capital gains, equitable estate etc.)
There are 2 sets of events that can trigger a succession plan: controllable and uncontrollable.
Controllable events
Sale: Who do you sell the business to?
-
Family member
-
Manager/Employees
-
Outside Party
-
There are advantages and disadvantages for each- it’s important to examine all channels.
Retirement: When do you want to retire?
-
What are the financial and psychological needs of the business owner?
-
Is there enough? Is there a need for capital to provide for retirement income, redeem or freeze shares?
-
Does this fit into personal/retirement plan? Check tax, timing, corporate structures, finances and family dynamics. (if applicable)
Uncontrollable Events
Divorce: A disgruntled spouse can obtain a significant interest in the business.
-
What portion of business shares are held by the spouse?
-
Will the divorced spouse consider selling their shares?
-
What if the divorced spouse continues to hold interest in the business without understanding or contributing to the business?
-
If you have other partners/shareholders- would they consider working with your divorced spouse?
Illness/Disability: If you were disabled or critically ill, would your business survive?
-
Determine your ongoing income needs for you, your spouse and family. Is there enough? If there is a shortfall, is there an insurance or savings program in place to make up for the shortfall amount?
-
Will the ownership interest be retained, liquidated or sold?
-
How will the business be affected? Does the business need capital to continue operating or hire a consultant or executive? Will debts be recalled? Does the business have a savings or insurance program in place to address this?
Death: In the case of your premature death, what would happen to your business?
-
Determine your ongoing income needs for your dependents. Is there enough? If there is a shortfall, is there an insurance or savings program in place to make up for the shortfall amount?
-
Will the ownership interest be retained, liquidated or sold by your estate? Does your will address this? Is your will consistent with your wishes? What about taxes?
-
How will the business be affected? Does the business need capital to continue operating or hire a consultant or executive? Will debts be recalled? How will this affect your employees? Does the business have a savings or insurance program in place to address this?
Execution: It’s good to go through this with but you need to get a succession plan done. Besides having a succession plan, make sure you have an estate plan and buy-sell/shareholders’ agreement.
Because a succession plan is complex, we suggest that a business owner has a professional team to help. The team should include:
-
Financial Planner/Advisor (CFP)
-
Succession Planning Specialist
-
Insurance Specialist
-
Lawyer
-
Accountant/Tax Specialist
-
Chartered Life Underwriter (CLU)
Next steps…
-
Contact us about helping you get your succession planning in order so you can gain peace of mind that your business is taken care of.