Starting a new business venture can be both exciting and nerve-racking at the same time. The hopes and dreams of success, financial freedom and being your own boss are accompanied by many uncertainties and risks. To add to some of the anxiety, comes the facts: about half of all new businesses will not be around within the next 5, and only about one third will survive 10+ years. The situation often becomes more complex when there are multiple owners and the future success of a business is at risk if proper planning is not done. The unexpected ‘exit’ of a partner due to death, disability, illness, retirement or just simply that ‘it’s not working out’ can create a very difficult situation for the remaining business owner(s) and the business itself. Many businesses operate under a ‘handshake’ sort of agreement, but those rarely are upheld when the situation starts to get challenging. In order to protect against all of these pitfalls, it is always advised to have the right structure in place to address any potential challenges that may arise. This is done through incorporating a Buy-Sell Agreement between the owners.
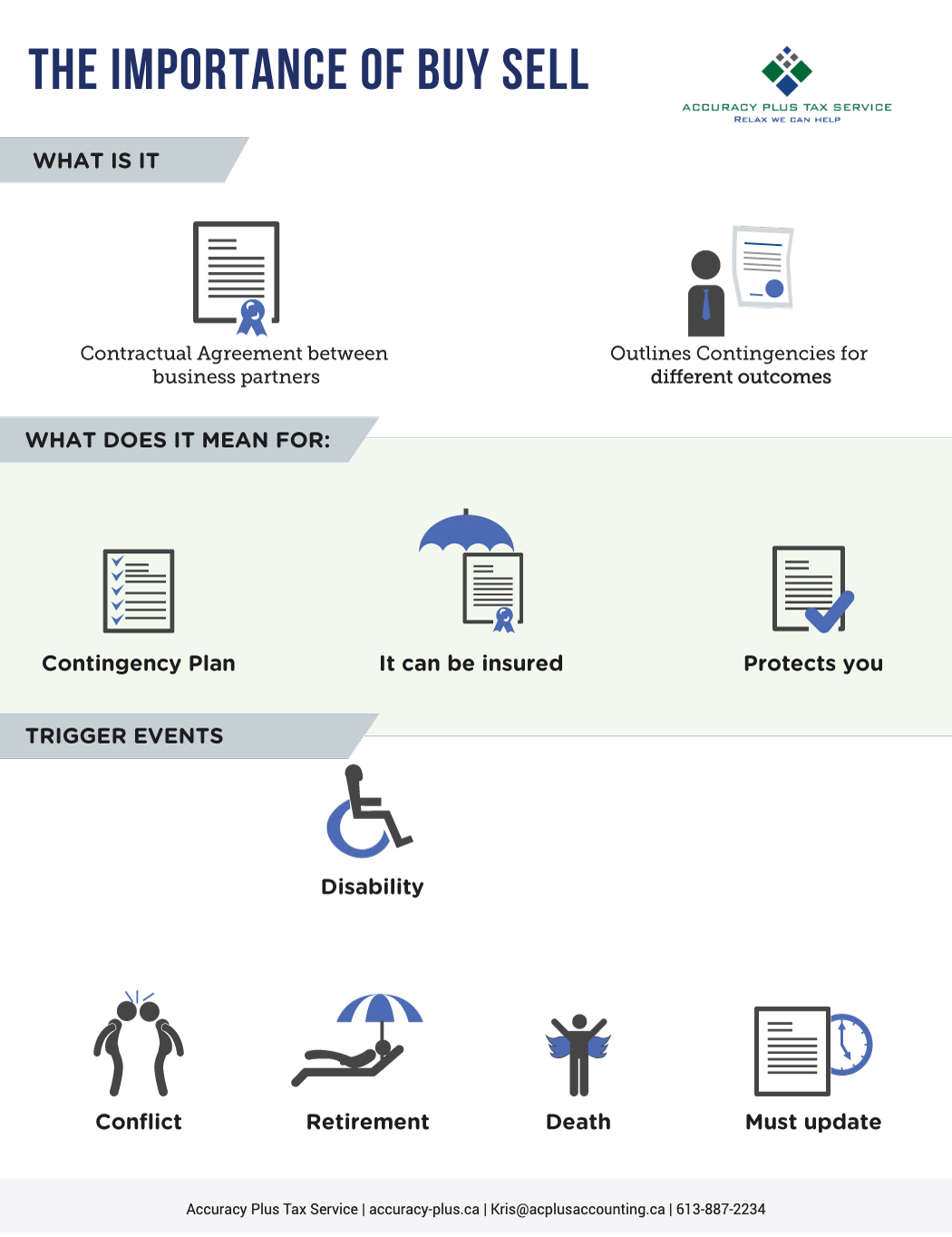
What is a Buy‐Sell Agreement?
A buy-sell agreement is a legally binding contract designed to establish a set of rules or actions for the remaining business owner(s) to carry on the business, in the event one of them is no longer involved in the business – this can be due to death, illness, injury, retirement or a simple desire to ‘get out’. In other words, this document dictates how the remaining owner(s) will interact with each other and how the business will operate when certain situations occur. This agreement creates certainty and a ‘game plan’ in case one or more of the partners are no longer able or willing to commit to the business.
Types of Buy‐Sell Agreements
Buy-sell agreements are generally structured as a cross purchase agreement, promissory note agreement, or a share redemption agreement.With a cross-purchase agreement, each shareholder within the agreement agrees to purchase a specified percentage of the shares owned by the departing shareholder, and if it’s due to death, the deceased shareholder’s estate is obligated to sell the shares to the remaining shareholder(s). A shareholder will generally purchase insurance on the life of the other shareholder(s) and on death, will use the proceeds from the insurance to buy out the remaining shares from the deceased shareholder’s estate.With a promissory note agreement, corporate owned life insurance is placed on the life of each shareholder, with the corporation named as the payor and beneficiary. In the event that a shareholder dies, the surviving shareholder(s) purchases the deceased’s shares from their estate using a promissory note. Once the remaining shareholder(s) owns the deceased shareholder’s shares, the company collects the death benefit on the insurance policy with the excess amount above the adjusted cost basis of the policy in the capital dividend account. The company then provides the surviving shareholder(s) a capital dividend which provides the remaining shareholder(s) the necessary funds to pay off the promissory note.Under the share redemption arrangement corporate owned life insurance is placed on the life of each shareholder with the corporation named as the payor and beneficiary. In the event that a shareholder dies, the company collects the insurance proceeds and places the excess amount above the adjusted cost basis of the policy in the capital dividend account. The company uses the proceeds in the capital dividend account to redeem the shares held by the deceased shareholder’s estate. Once that is done, the remaining shareholder(s) takes over the ownership of those purchased shares.Each structure has their advantages and disadvantages and should be reviewed with a legal professional, tax professional as well as a knowledgeable Financial Advisor.
Why the business needs a buy‐sell agreement
A buy-sell agreement is a crucial component of a business that should be incorporated to protect the shareholders as well as the business itself. It is designed to ensure important things are taken care of if someone leaves the business for whatever reason, so that the business can continue to grow and run successfully. A buy-sell agreement offers several key benefits to your business:
-
It maintains the continuity of your business by ensuring members get to decide what happens to the business before any problems arise.
-
It protects company ownership by laying out a succession plan for departing members. This keeps remaining shareholders from being burdened by untested and unproven successors (like the widow or children of the departing co-owner).
-
It minimizes dispute between remaining co-owners and the family of the departing owner by having a strategy in place ahead of time to govern business operations.
-
It alleviates co-owner stress and uncertainty by specifically identifying which events would trigger a buyout.
-
It protects business assets and liquidity by providing a financial (and tax) plan for each of the different triggers addressed in the agreement.
-
It protects the interest of, not just the business entity itself, but also that of the business owners to ensure members (and their families, in the event of death or disability) are handled with respect, courtesy and the utmost fairness.
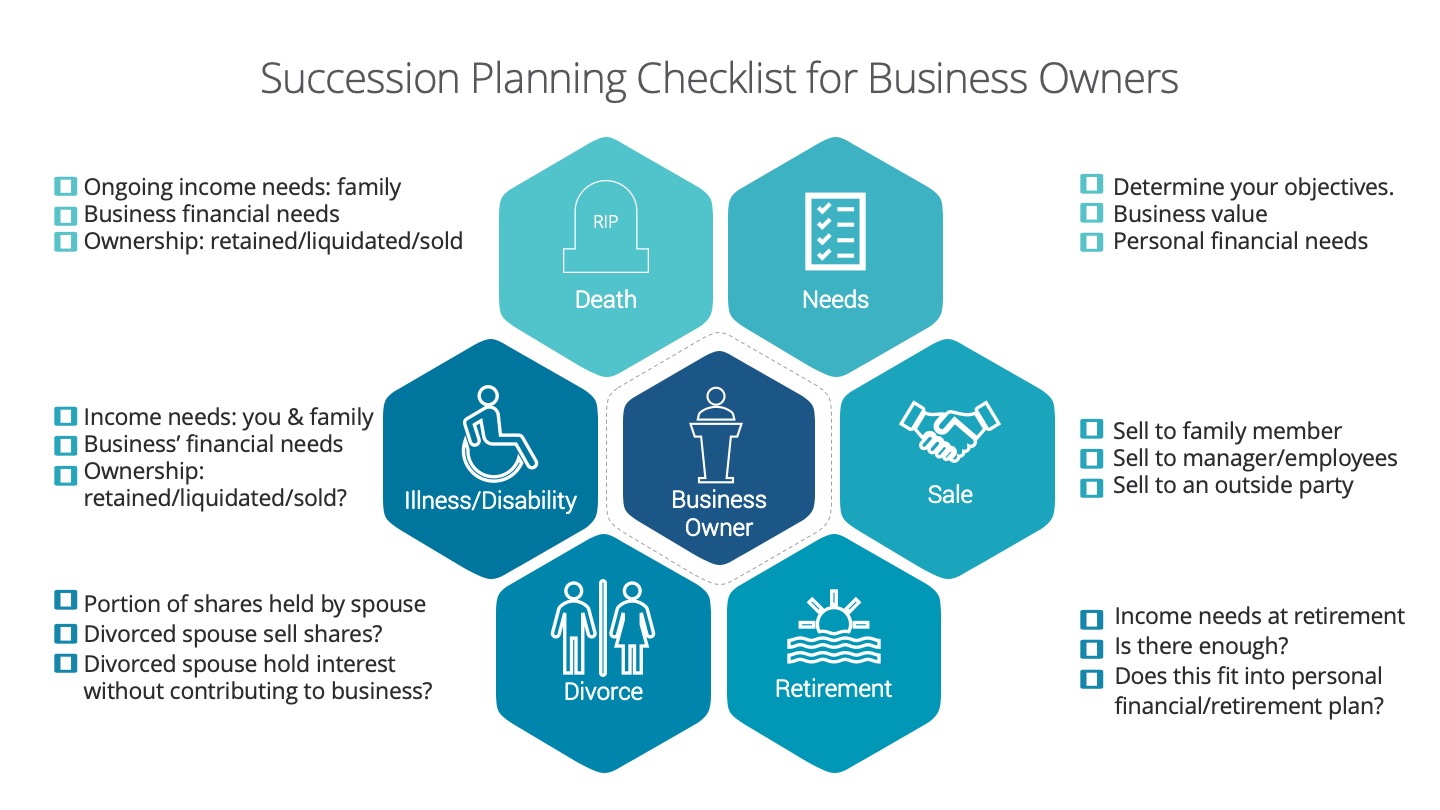
What to include in the buy‐sell agreement
Since a buy-sell agreement is a legally binding document, it generally should be drafted with a knowledgeable and experienced Legal Professional. Most agreements are started through a generic template, but then are customized for the needs of each business/partner and can be a fairly thorough and comprehensive document. There are several different components of a buy-sell agreement and several different aspects need to be addressed, such as the valuation of the company, ownership interests, buy-out clauses, and terms of payment. The agreement should generally be drafted at the very start of the business, so as to avoid any issues or misunderstandings later on. The agreement will also address certain ‘triggering events’, which are listed below.
Disagreement
Conflict between owners of a business in regards to the direction or management of the business can sometimes occur, and can even push the most successful business off-course. In a situation where no agreement or mediation can be reached, it may make sense to allow for one or more of the partners to be bought out. This would allow the business to continue moving forward and is often referred to as a ‘shot-gun clause’. Sometimes a situation where one owner offers to buy-out the other would also offer to be bought-out for the same value, thus ensuring fair treatment and value of the shares.
Divorce
An owner who is in the midst of a divorce may be bought-out by other partners, to protect the company ownership. A divorce settlement will generally depend on the partner’s share of the business. It’s not uncommon for a family law judge to order a business owner to split his or her interest in a company with the former spouse. To protect the business from this event, a clause should require the shares held by the former spouse of a partner to be acquired by the company or one of the other owners.
Retirement
The value of the business comprises a significant component for the retirement of many business owners. Allowing the remaining partners to reclaim the interest in the business keeps the business intact and provides the retiring partner with a market to liquidate their ownership, thus providing the retiring partner with a cash infusion to enjoy their retirement. There may also be some distinction in the agreement between early retirement and regular retirement and how the shares of the departing owner are to be valued.
Bankruptcy
Borrowing money to expand or grow the company, or to purchase equipment or goods, is common for many companies. However, lending institutions often require personal guarantees from the owners/shareholders of the business. Having one or more owners that are not able to provide this guarantee can lead to higher fees and impact the overall financial well-being and growth of the business. Therefore, a provision should be considered to allow the other shareholders the opportunity to acquire shares of the defaulting shareholder(s).
Disability
An owner who has become disabled and unable to perform their duties can impact the overall well-being of the business. The agreement should address several situations and questions, such as whether the partner will continue to receive a salary, and for how long, or whether they will continue in the day-to-day management of the company.The buy-sell agreement also needs to clearly define what is considered a disability and should include a timeline for which the disabled partner would be given the opportunity to return. Often the business will purchase disability buy-sell insurance and link the definitions to the plan. This has the added benefit of providing an independent third party to determine when the criteria for the buy-out are satisfied.
Death
The death of a partner is an unfortunate and difficult situation for both the family and business partners alike. To deal with the stress of continuing the business, establishing the rules of business continuity upon death provides peace of mind to both the surviving partners and the family of the deceased. The surviving partners benefit from the assurance of not having to deal with an unwanted partner and the family is assured that they will be treated fairly.Generally, all partners/co-owners will be covered by a ‘key person’ life insurance policy, which can be paid by either the company or the other partners, where the death benefit would be used to buy out the deceased owner’s shares (as mentioned above).
Funding the buy‐sell agreement
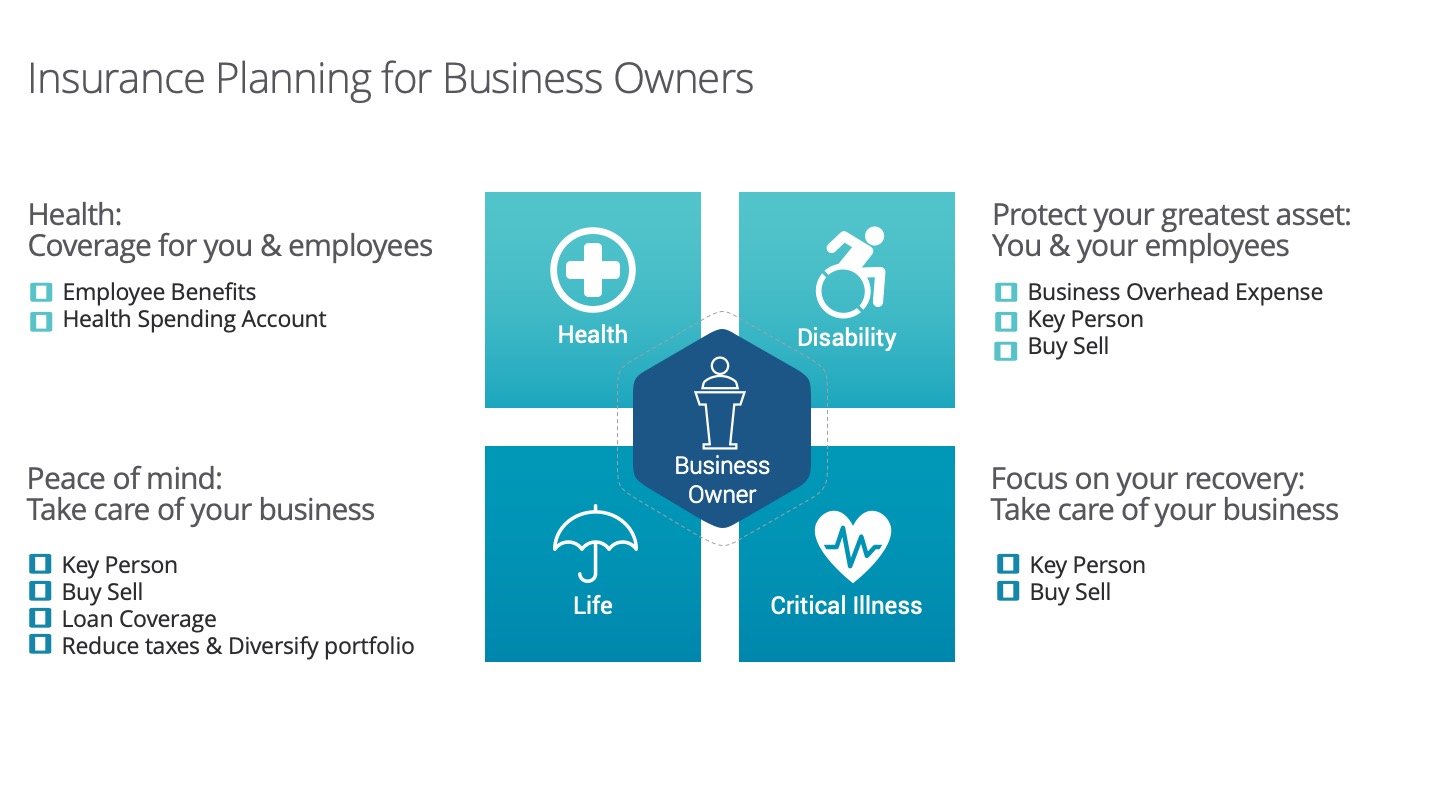
Without sufficient resources to fund a potential buy-out, the agreement itself can fall apart. The partners need to decide where the money will come from to complete the buy-out – whether it will be the responsibility of individual owners or from the company itself. While not all events can be protected, two can: the death and disability of a shareholder. By using an insurance policy, funds can be made available at the time they are needed, thus minimizing potential liquidity issues, protecting the business and the impacted shareholders, as well as the family of the deceased shareholder. Using insurance provides the protection needed at a fraction of the cost to the alternatives and can provide immediate capital and significant tax benefits.
Working as a partnership between 2 or more individuals is never an easy task, and the situation only gets more complicated when one or more of them exits the business. Protecting not only the business, but your personal interests, as well as your family’s future are very important objectives for any business owner, and should not be overlooked. Although no business can be certain of success, there are strategies and structures that can help protect the business from failure in the future. Working with a knowledgeable and experienced Financial Advisor, Legal Professional and Tax Professional, you can be assured that you can have the proper Buy-Sell Agreement in place so that all parties involved benefit.